
Industry expert Joe Nasvik summarizes ins and outs of updated regulations
The U.S Department of Labor will begin to enforce its new concrete silica dust ruling on Sept. 23. It’s important to be up-to-date on all the new changes regarding these new OSHA standards. To help ease the transition, Bosch Power Tools partnered with industry expert Joe Nasvik to outline everything contractors and superintendents need to know prior to the Sept. 23 deadline.
(Q): What is the new silica dust regulation and why is it happening?
When the U.S. Department of Labor issued its ruling aimed at better protecting workers from respirable silica dust, no one was surprised. Compliance with the new rule went into effect June 23, 2017, and enforcement begins Sept. 23, 2017. The upgraded regulation substantially reduces the permissible exposure limits for workers in the construction industry. The Department of Labor’s Occupational Safety and Health Administration will enforce a reduction in the amount of silica that workers can be exposed to over an eight-hour day from 250 micrograms per cubic meter of air to 50 micrograms.
(Q) What exactly is silica?
Silicon is the second most common element on earth, making up 28 percent of the planet’s crust. Oxygen is the most common element at 47 percent and aluminum is a distant third at eight percent. Silicon combines with oxygen to form quartz – an example being sand. Silica is a component in a wide range of the earth’s rock.
(Q) Is respirable crystalline silica a threat to life?
Inhalation of respirable crystalline silica is a threat to life. Particles can be created by natural forces such as wind, which causes particles to collide and form smaller particles. According to OSHA, it’s estimated that 2.3 million U.S. workers are exposed to respirable silica dust at work each year.
(Q) But aren’t there already OSHA regulations in place to limit silica exposure?
OSHA set limits on respirable crystalline silica dust exposure in 1971, shortly after the agency was created. These regulations, based on research from the 1960s and earlier, soon showed that they didn’t adequately protect workers. The limits were imposed as formulas that many people found difficult to understand. The new rule limits the amount of silica dust that workers can be exposed to on the job to 50 μg/m3 averaged over an eight-hour shift for all industries covered by the rule. That’s about 1/20th the size of a grain of salt.
(Q) So what should contractors and people on the jobsite do to avoid silica dust exposure?
Employers are required to use “engineering controls,” such as vacuum dust collection systems and water-delivery systems to limit worker exposure to respirable silica dust and use respirators as required. Specified exposure control methods are referenced in OSHA Table 1.
(Q) How do I know what tools I need for the job I’m doing?
At the heart of the new silica dust control regulations is OSHA Table 1, noted previously. Table 1 matches common construction tasks with effective dust control methods for those tasks. The table has three columns: the task or equipment being used, a column describing the method for controlling dust and a third column stating what type of respiratory protection is needed when performing the task. By finding a work activity on the table, it’s easy to determine what steps are necessary to ensure compliance.
(Q) Then what’s the alternative? What are power tool manufacturers doing to help solve this?
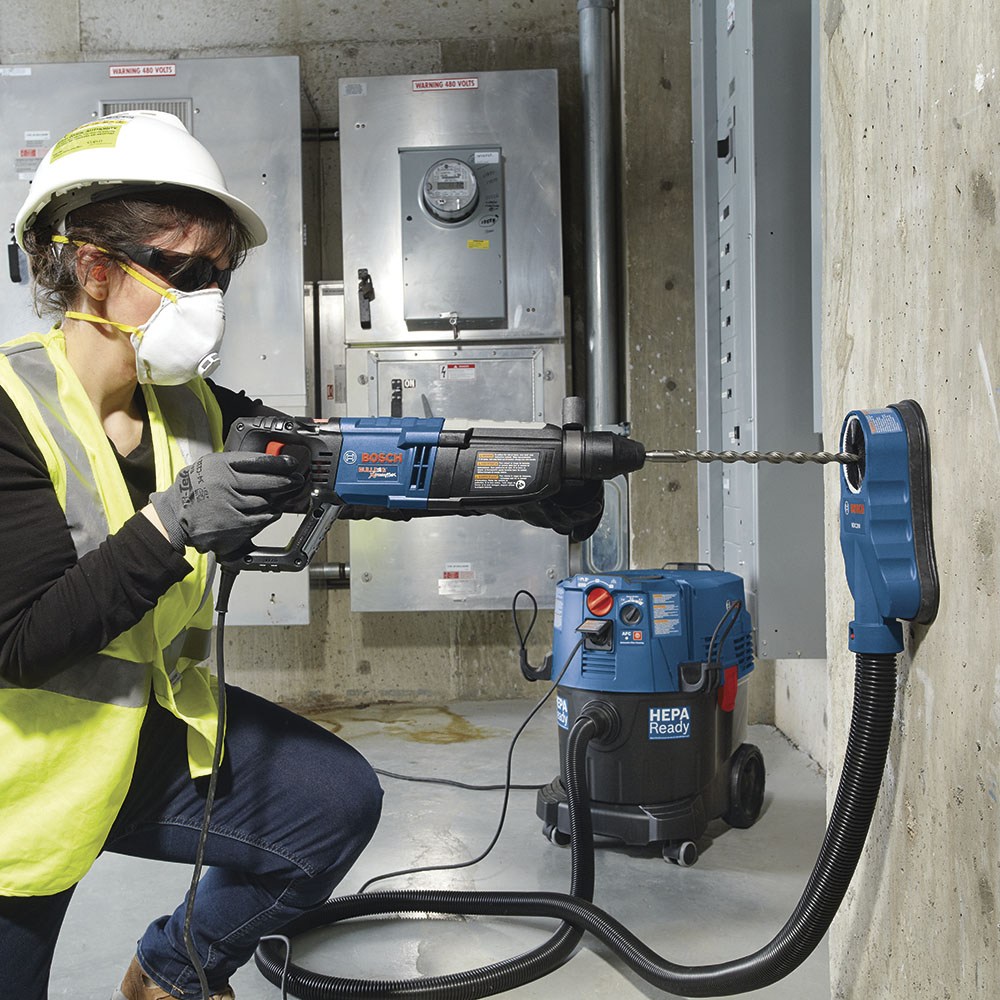
The best way to control respirable crystalline silica dust is to remove it as it’s created. Power tool manufacturers have developed products and systems to help meet OSHA requirements for limiting silica dust exposure. The focus is on developing better dust extractors and attachments, such as shrouds, to capture dust at the source.
(Q) How are concrete workers supposed to capture dust so it doesn’t become airborne?
For most concrete applications, tool attachments that confine dust are connected to vacuums to prevent particles from becoming airborne. These systems represent a primary method for keeping the air clean. Attachments include shrouds for grinders and dust extraction attachments that fit around chipping hammer bits and hammer drill bits. Another component specifically for drilling concrete is dust extraction bits. The bit allows dust created at the bottom of a hole being drilled to be sucked through the center of the bit and collected in the dust extractor.
In addition, employers must create processes that minimize release of respirable silica dust into the environment during maintenance of tools and employee change of work clothes.
(Q) So, I just connect these accessories to my regular vacuum in the shop?
No. The vacuum needs to have a high amount of cfm suction (+150), a filter cleaning feature built in and it is ideal for them to be HEPA compliant. To qualify as HEPA, U.S. government standards require that the air filter remove 99.97 percent of particles with a size of three microns or less. HEPA filters are expensive, but necessary for removing small particles. When looking for a HEPA vacuum filter that meets OSHA requirements, it must state on the filter that it will remove particles three microns in size or less. As a filter removes smaller and smaller particles, the power and airflow of the vacuum, as measured in cubic feet per minute, must increase.
(Q) How do you clean these specialty filters to make sure the vacuum still functions properly?
OSHA requires vacuum filters to function properly at all times. For vacuums intended for concrete/fine dust collection, certain vacs provide a feature that automatically cleans the filter every 15 seconds with reverse blasts of air to ensure the filter maintains its utility. Various manufacturers employ different filter-cleaning methods. Filters should never be washed out, especially when concrete dust is involved because it will harden in the filter pores and render the filter useless.
(Q) This is a lot to digest (enforcement date is Sept. 23). How will this affect productivity when we’re trying to finish a job?
The enforcement date varies by state, but for the majority Sept. 23 is the date. This entire effort ties back to keeping people safe. There is no cure for silicosis or other silica-related diseases, so worker health depends on limiting exposure. Although regulation is sometimes viewed as limiting productivity, in this instance it can actually be enhanced. The respirable silica dust regulations require use of already accepted control methods that make implementation easier.
For more info, visit: https://www.osha.gov/silica/.
Photos courtesy of Bosch Power Tools.





 Join our thriving community of 70,000+ superintendents and trade professionals on LinkedIn!
Join our thriving community of 70,000+ superintendents and trade professionals on LinkedIn! Search our job board for your next opportunity, or post an opening within your company.
Search our job board for your next opportunity, or post an opening within your company. Subscribe to our monthly
Construction Superintendent eNewsletter and stay current.
Subscribe to our monthly
Construction Superintendent eNewsletter and stay current.