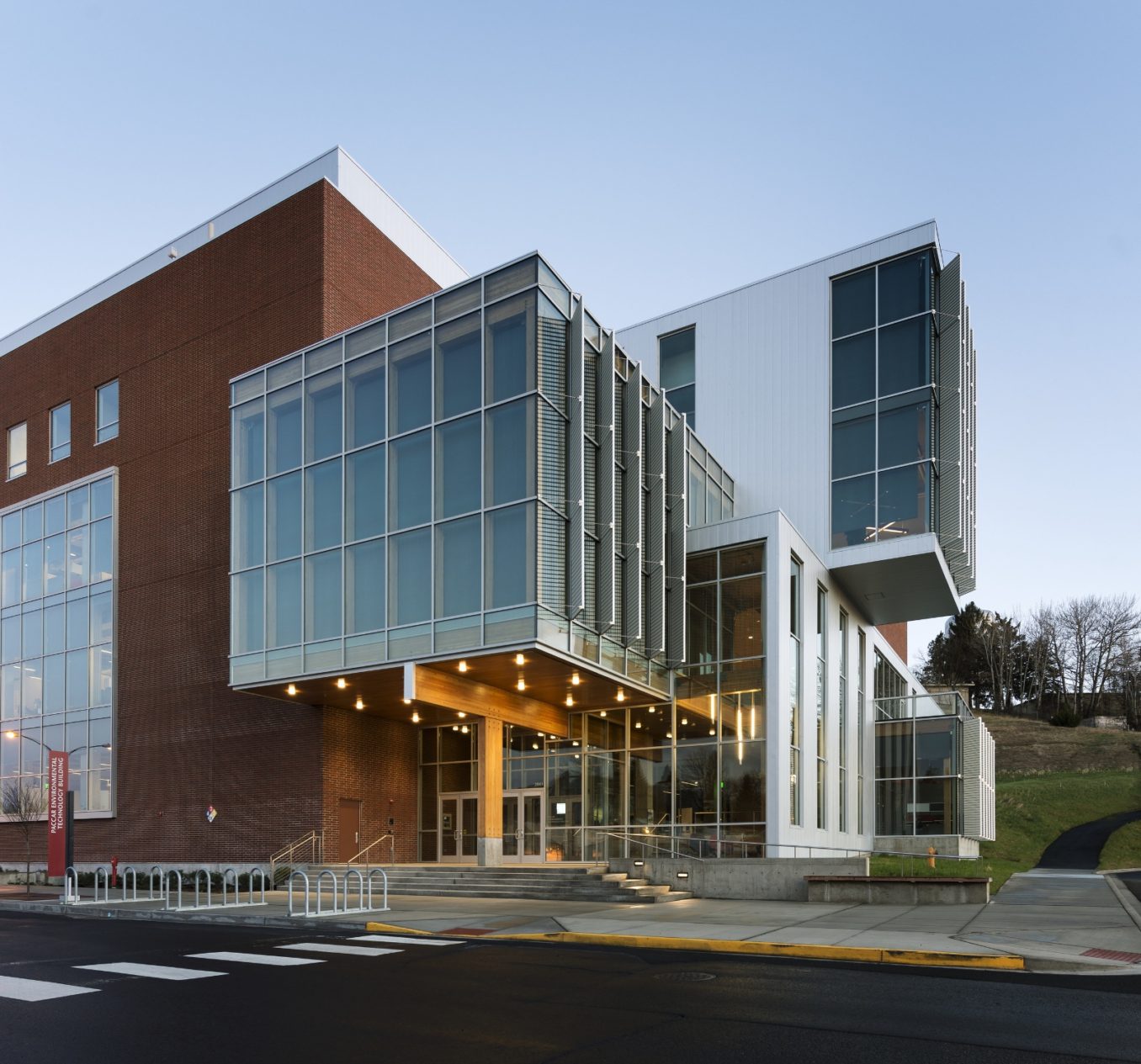

SEATTLE, Wash. – The $52.8-million PACCAR Environmental Technology Building at Washington State University in Pullman, Washington has recently opened. The 96,000-square-foot project, a collaboration between designers LMN Architects and general contractor Skanska, brings to life the vision of WSU’s Voiland College of Engineering and Architecture and the pursuit of interdisciplinary research related to sustainability concerns.
The new four-story building serves five of WSU’s long-standing research and development centers, all dedicated to tackling multi-faceted environmental issues through interdisciplinary collaboration. “What’s exciting about this project is how it sums up so much of what contemporary education is about—collaboration, exploration…a true interdisciplinary approach—the whole project is essentially one giant laboratory,” notes Mark Reddington, FAIA, partner at LMN.
Conceptually, the building merges the spirit of collaboration with the exploration of materiality. Functionally, the building is formed by two distinct elements: a “workhorse bar” housing secure laboratories, offices and student workstations; and a “showcase bar” that presents the program’s work to the campus community with transparent program spaces, including a heavy materials lab, a double-height seminar room and a flexible design studio. The intersection of the two bars creates a “Town Square,” a lounge and cafe that serve as the social hub of the program and where the general public and researchers can intermingle and enjoy views of the campus, the Palouse, and the active spaces.
The western portion of the building, including the Simpson Strong-Tie Research and Testing Laboratory, is framed in engineered wood products including cross-laminated timber, as well as glue-laminated timber and laminated-veneer lumber. The history of these engineered wood products is intricately tied to WSU. One of the research centers, the Composite Materials and Engineering Center, is the modern successor to the Wood Materials and Engineering Laboratory, which was founded at WSU in 1949 and was instrumental in the development of the billion-dollar industry of up-cycling wood waste from the timber industry.
Captured rainwater satisfies 85 percent of the non-potable water demand, and daylight is calibrated through digitally modeled sunshades making glare-free, panoramic views possible. The project anticipates LEED Gold certification.
Photos courtesy of LMN.



 Join our thriving community of 70,000+ superintendents and trade professionals on LinkedIn!
Join our thriving community of 70,000+ superintendents and trade professionals on LinkedIn! Search our job board for your next opportunity, or post an opening within your company.
Search our job board for your next opportunity, or post an opening within your company. Subscribe to our monthly
Construction Superintendent eNewsletter and stay current.
Subscribe to our monthly
Construction Superintendent eNewsletter and stay current.