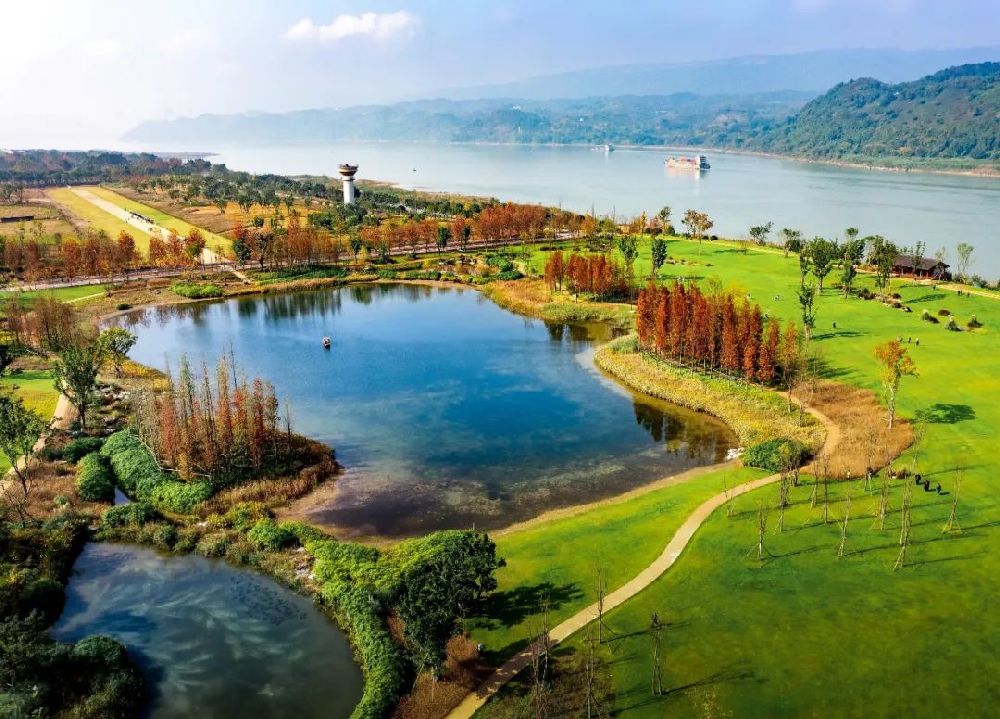

The second phase of the ecological restoration project on Guangyang Island in Chongqing, China has been completed. China State Construction Engineering Corporation served as the builder on the project.
Expanding on the positive outcomes of the first phase, the second phase centers on a comprehensive approach, incorporating island-wide conservation efforts, while refining the accomplishments of the first phase. This inclusive ecological restoration model encompasses mountainous, flat and sloped regions, with the overall restoration covering an area of about 9.67 square kilometers.
The project team implemented island-wide conservation, restoration and slope management, addressing the distinct characteristics of mountainous, flat and sloped terrains. They erected complementary ecological structures, green buildings and supportive facilities, contributing to the comprehensive enhancement of the island’s ecological restoration.
Tailoring their approach to the local environment, the project team identified zones for ecological protection and restoration. They safeguarded over 4,100 acres of mountainous terrain, repaired an additional 380 acres, conserved and rehabilitated 127 hectares of forest land and introduced a diverse array of over 60,000 trees, establishing a distinctive mountainous forest ecosystem.
In an innovative move, the project team introduced a “three-line” technology designed for water quality protection on Guangyang Island, enabling a sustainable circulation of the island’s water system. This initiative reinstated the island’s capacity to naturally accumulate, permeate and purify rainwater.
By implementing artificial restoration techniques, the team added native vegetation, environmentally revamped the existing city roads, redesigned the landscape, enhanced soil quality and rehabilitated farmland. Across 23.7 hectares, they cultivated a variety of crops and vegetables, dedicated 8.7 hectares to grass, allocated 1.4 hectares for traditional Chinese medicinal herbs and planted over 10,000 fruit trees, resulting in the development of a thriving ecological landscape with fertile fields.
The project team undertook the dredging of nine lakes and subsequently implemented basal improvements, anti-seepage measures and shoreline restoration, overseeing the management of 17.7 hectares of lakes and ponds. This accomplishment brought the island’s water quality in line with the Class II of China’s surface water quality standard.
Following a “three-step” model involving solid soil protection, stable vegetation and rich biodiversity, the team pursued a phased-restoration approach in vertical, horizontal and temporal dimensions. They effectively managed the submerged area.
After ecological restoration, the island experienced a surge in plant species from 383 to 627 and an increase in animal species from 310 to 458, culminating in the restoration of the riparian ecosystem’s authenticity and integrity.
Presently, Guangyang Island showcases a charming rural panorama, characterized by undulating waves, breathtaking scenery and a serene coexistence of people and nature in countryside.









 Join our thriving community of 70,000+ superintendents and trade professionals on LinkedIn!
Join our thriving community of 70,000+ superintendents and trade professionals on LinkedIn! Search our job board for your next opportunity, or post an opening within your company.
Search our job board for your next opportunity, or post an opening within your company. Subscribe to our monthly
Construction Superintendent eNewsletter and stay current.
Subscribe to our monthly
Construction Superintendent eNewsletter and stay current.